Introduction to Cathode Ray Tube:
Cathode ray tube is a display device that is used for displaying an electrical signal upon two-dimensional display screens by using principle of fluorescence that is resulted from reaction of electrons and fluorescent chemicals. It is very important part of cathode ray oscilloscope being like heart of whole oscilloscope system.
What are the parts of Cathode ray tube?
1. Electron gun assembly
2. Deflection plate assembly for deflection of electron beam
3. Fluorescent screen for production of displaying
4. Glass envelope to assemble whole cathode ray tube
5. Base to provide connection to external circuitry
The following figure shows the main part of cathode ray tube. Before we go to study all these parts in detail it will be suitable to have some basic knowledge regarding the function of these parts on individual and constitutive basis.
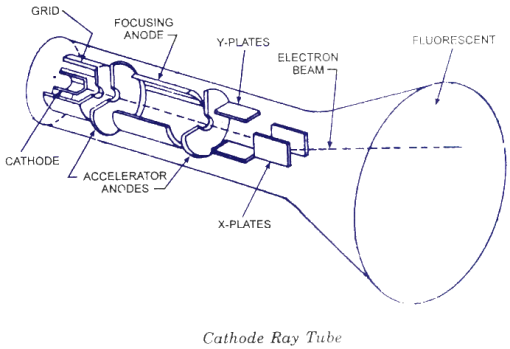
Operation of CRT:
Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) is a computer display screen, used to display the output in a standard composite video signal. The working of CRT depends on movement of an electron beam which moves back and forth across the back of the screen. The source of the electron beam is the electron gun; the gun is located in the narrow, cylindrical neck at the extreme rear of a CRT which produces a stream of electrons through thermionic emission. Usually, A CRT has a fluorescent screen to display the output signal. A simple CRT is shown in below.
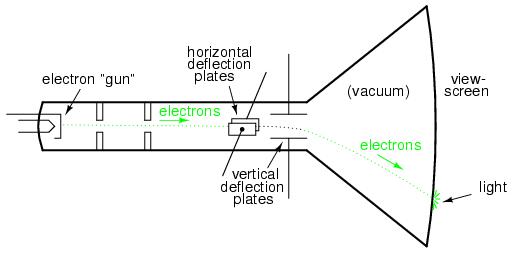
The operation of a CRT monitor is basically very simple. A cathode ray tube consists of one or more electron guns, possibly internal electrostatic deflection plates and a phosphor target. CRT has three electron beams – one for each (Red, Green, and Blue) is clearly shown in figure. The electron beam produces a tiny, bright visible spot when it strikes the phosphor-coated screen. In every monitor device the entire front area of the tube is scanned repetitively and systematically in a fixed pattern called a raster. An image (raster) is displayed by scanning the electron beam across the screen. The phosphor’s targets are begins to fade after a short time, the image needs to be refreshed continuously. Thus CRT produces the three colour images which are primary colors. Here we used a 50 Hz rate to eliminate the flicker by refreshing the screen.
Main parts of the cathode ray tube are cathode, control grid, deflecting plates and screen.
Cathode:
The heater keeps the cathode at a higher temperature and electrons flow from the heated cathode towards the surface of the cathode. The accelerating anode has a small hole at its centre and is maintained at a high potential, which is of positive polarity. The order of this voltage is 1 to 20 kV, relative to the cathode. This potential difference creates an electric field directed from right to left in the region between the accelerating anode and the cathode. Electrons pass through the hole in the anode travel with constant horizontal velocity from the anode to the fluorescent screen. The electrons strike the screen area and it glows brightly.
The Control Grid:
The control grid regulates the brightness of the spot on the screen. By controlling the number of electrons by the anode and hence the focusing anode ensures that electrons leaving the cathode in slightly different directions are focused down to a narrow beam and all arrive at the same spot on the screen. The whole assembly of cathode, control grid, focusing anode, and accelerating electrode is called the electron gun.
Deflecting Plates:
Two pairs of deflecting plates allow the beam of electrons. An electric field between the first pair of plates deflects the electrons horizontally, and an electric field between the second pair deflects them vertically, the electrons travel in a straight line from the hole in the accelerating anode to the centre of the screen when no deflecting fields are present, where they produce a bright spot.
Screen:
This may be circular or rectangular. Screen is coated with special type of fluorescent material. Fluorescent material absorbs its energy and re-emits light in the form of photons when electron beam hits the screen. When it happens some of them bounces back just like bouncing of cricket ball from a wall. These are called as secondary electrons. They must be absorbed and returned back to cathode, if it is not so they accumulate near screen and produce space charge or electrons cloud. To avoid this, aquadag coating is applied on funnel part of CRT from inside.
Advantages of CRT:
- CRT’s are less expensive than other display technologies.
- They operate at any resolution, geometry and aspect ratio without decreasing the image quality.
- CRTs produce the very best color and gray-scale for all professional calibrations.
- Excellent viewing angle.
- It maintains good brightness and gives long life service.
Features of CRT:
The use of CRT technology has quickly declined since the introduction of LCDs but they are still unbeatable in certain ways. CRT monitors are widely used in a number of electrical devices such as computer screens, television sets, radar screens, and oscilloscopes used for scientific and medical purposes.
