Introduction to Arrays
An array is a collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations. The idea is to store multiple items of the same type together. Instead of declaring individual variables, such as number0, number1, …, and number99, you declare one array variable such as numbers and use numbers[0], numbers[1], and …, numbers[99] to represent individual variables. This makes it easier to calculate the position of each element by simply adding an offset to a base value, i.e., the memory location of the first element of the array (generally denoted by the name of the array). The base value is index 0 and the difference between the two indexes is the offset.
For simplicity, we can think of an array as a fleet of stairs where on each step is placed a value (let’s say one of your friends). Here, you can identify the location of any of your friends by simply knowing the count of the step they are on.
Remember: “Location of next index depends on the data type we use”.
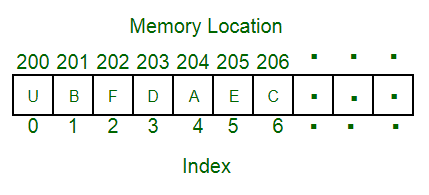
The above image can be looked at as a top-level view of a staircase where you are at the base of the staircase. Each element can be uniquely identified by its index in the array (in a similar way as you could identify your friends by the step on which they were on in the above example).
