What is the Compton Effect?
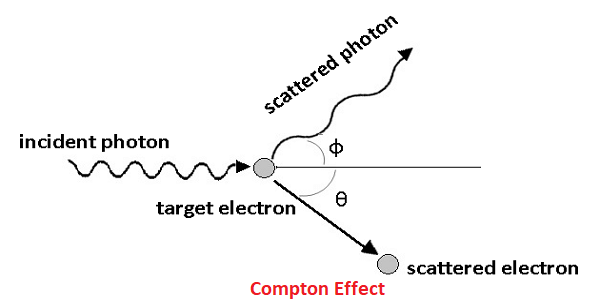
A. H. Compton observed that “when a monochromatic beam of high frequency (lower wavelength) radiation (e.g., X-rays and γ-ray) is scattered by a substance, the scattered radiation contains two types of wavelengths one having the same wavelength as that of incident radiation while the other having the wavelength greater (or lower frequency) than that of incident radiations. This effect is known as Compton Effect.
Quantum Explanation: The explanation was given by Compton which was based on the quantum theory of light. According to the quantum theory when a photon of energy hυ strikes the substance some of the energy of the photon is transferred to the electrons, therefore the energy (or frequency) of the photon reduces, and wavelength increases.
Various assumptions were made for explaining the effect these were:
(i) Compton Effect is the result of the interaction of an individual particle and free-electron of the target.
(ii) The collision is relativistic and elastic.
(iii) The laws of conservation of energy and momentum hold good.
