Enumeration/Enumerated data types
Enumeration(or enum or Enumerated data type) is a user-defined data type in C. It is mainly used to assign names to integral constants, the names make a program easy to read and maintain.
enum State {Working = 1, Failed = 0};
The keyword ‘enum’ is used to declare new enumeration types in C and C++. Following is an example of enum declaration.
// The name of enumeration is "flag" and the constant
// are the values of the flag. By default, the values
// of the constants are as follows:
// constant1 = 0, constant2 = 1, constant3 = 2 and
// so on.
enum flag{constant1, constant2, constant3, ....... };
Variables of type enum can also be defined. They can be defined in two ways:
// In both of the below cases, "day" is
// defined as the variable of type week.
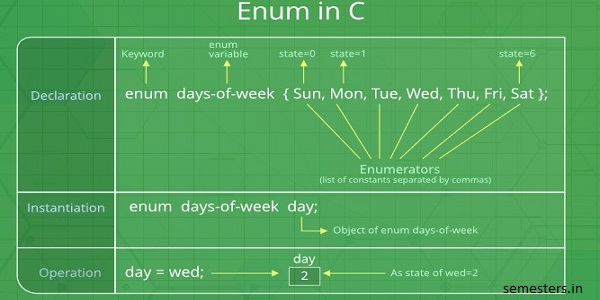
enum week{Mon, Tue, Wed};
enum week day;
// Or
enum week{Mon, Tue, Wed}day;
// An example program to demonstrate working // of enum in C #include<stdio.h> enum week{Mon, Tue, Wed, Thur, Fri, Sat, Sun}; int main() { enum week day; day = Wed; printf("%d",day); return 0; |
Output:
2
In the above example, we declared “day” as the variable and the value of “Wed” is allocated to day, which is 2. So as a result, 2 is printed.
Another example of enumeration is:
// Another example program to demonstrate working // of enum in C #include<stdio.h> enum year{Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, Dec}; int main() { int i; for (i=Jan; i<=Dec; i++) printf("%d ", i); return 0; } |
Output:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
In this example, the for loop will run from i = 0 to i = 11, as initially the value of i is Jan which is 0 and the value of Dec is 11.
