COMPETITIVE ENVIRONMENT
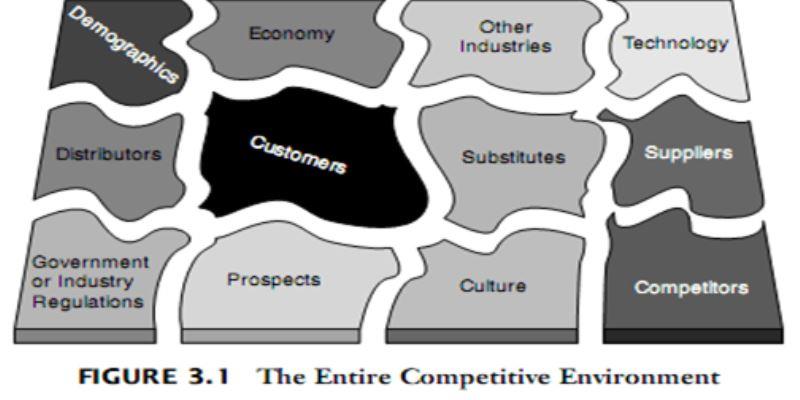
A competitive environment is the dynamic external system in which a business competes and functions. The more sellers of a similar product or service, the more competitive the environment in which you compete. Look at fast food restaurants – there are so many to choose from; the competition is high.
The competitive environment, also known as the market structure, is the dynamic system in which your business competes. The state of the system as a whole limits the flexibility of your business. World economic conditions, for example, might increase the prices of raw materials, forcing companies that supply your industry to charge more, raising your overhead costs. At the other end of the scale, local events, such as regional labor shortages or natural disasters, also affect the competitive environment.
Examples:
There are several examples of competitive business environments. The first that comes to mind is smart phones. How many choices do you have when it comes to buying a smart phone? They seemed to have multiplied overnight! That is an extremely competitive business environment.Companies are constantly trying to one-up the latest best-selling model – a good indication of a competitive environment. Additionally, prices of comparable smart phone models are relatively close.

Another competitive business environment is the automobile industry. Again, almost every company produces a car in every category. Therefore, when someone is looking at buying a new hybrid sedan or full-size truck, they have so many options to choose from. Obviously, the automobile industry can be segmented in economical and luxury brands, but when comparing within the same segment, there is significant competition.
Direct Competitors
Your direct competitors provide products or services similar to yours. For example, a small computer repair business competes with other local computer repair businesses, as well as large retail stores that offer computer repair services. Small retail shops compete with warehouse clubs and big-box retail stores that use their huge buying power to lower overhead costs, enabling them to offer steep discounts that small stores can’t afford.
Direct competitors are businesses that are selling the same type of product or service as you. For example, McDonalds is a direct competitor with Burger King. Indirect competitors are businesses that still compete even though they sell a different service or product. The products or services offered by indirect competitors tend to be those that can be substituted for one another. Again, considering travel, you have the option to travel by plane, train, or car. Therefore, airlines are also competing with train lines and buses (assuming the travel does not go overseas).
Indirect Competitors
In addition to direct competitors, some businesses also face competition from providers of dissimilar products or services. For example, a fine dining restaurant competes with other local restaurants, but it also competes with nearby supermarkets that offer ready-to-eat meals. And a pottery studio that relies heavily on children’s birthday parties must compete with other family-friendly establishments that offer children’s activities, such as roller rinks, theme restaurants and children’s museums.
Strategy
Calvin can utilize several different strategies to defeat his competition. Calvin will have a competitive advantage if two conditions are met:
- Potential customers perceive a difference between his app and the apps of his competitors.
- The perceived difference is important to potential customers, resulting in their selection of Calvin’s app.
Indicator of Competitive Advantage
A business organization with a competitive advantage is more profitable than its rivals while this profitability exceeds its cost of capital. Profits in excess of the cost of capital are called economic rent. Sustained economic rents are prima facie evidence of a competitive advantage.
Elements of Competitive Advantage :
- Uniqueness – finding unique opportunities and solutions is about imagination, insight, foresight, and the courage to pursue it. Unique is new, different, but most important of all, untested and unproven. By the time a unique solution is validated as profitable, it is no longer unique for the next company. Also, if it is a unique business model or business capability, it is likely unapproachable, in the short-term, by competitors.
- Strategic Focus – Strategic focus comes about from marrying distinctive competency and purpose to form a superior value proposition. Strategic focus is about developing a longer view of competitive advantage with a combination of purpose, competency, and value proposition. This creates an internal environment that has the confidence and implicit support to continue to perfect and develop that focus through creating stronger competencies and further perfecting the value proposition.
- Strategic Intent/Vision/BHAGs – Strategic intent challenges and guides the organization to achieve the unachievable by having a clear focus on outlandish objectives which require the development of new capabilities to achieve.
- Innovation – Innovation is inventiveness put into profitable practice. In an evolving economy, the business organization must innovate at a rate that meets or exceeds its environment in order to sustain a competitive advantage.
- Continual Innovation – Making innovation as an ongoing process on all fronts.
- Democratic Principles – Democratic principles are needed to fully engage the active participation of diverse thinkers from across the organization. Broad and diverse participation improves innovation.
- Strategic Management as a self-improving learning process – Strategic management must become, amongst other things, a learning and self-improvement process for the organization.
- Dynamic Capabilities – Sustainable competitive advantage is ultimately based on dynamic capabilities, the capability to produce and utilize new capabilities on a continuous basis.
It’s effect on INDIA-
-
India’s Changing Innovation System
The dual faces of its economy define India’s great innovation challenges. On the one hand, India is a global leader in information technology and business-process outsourcing services, which account for nearly $60 billion in annual exports and employ more than 2.5 million,
For the Indian government, however, the most urgent priorities in science and technology policy have been basic economic development. Although India’s economic growth rate has accelerated sharply since 2003, the benefits of India’s dynamic technology sectors have been slow to make a difference in the lives of hundreds of millions of people living in poverty. India is not just focused on improving its capacity to create new products, therefore. The Indian Government also now is paying more attention to what it calls “inclusive innovation,” which is defined as “using innovation as a tool to eliminate disparity and meet the needs of the many.
-
Reforming National Laboratories
-
Upgrading Higher Education
-
Developing Strategic Sectors
-
Focusing on Inclusive Innovation
-
India’s Innovative Companies
-
Public-Private Innovation Partnerships
-
Multinationals R&D Centers
-
Seeking Global Partnerships
