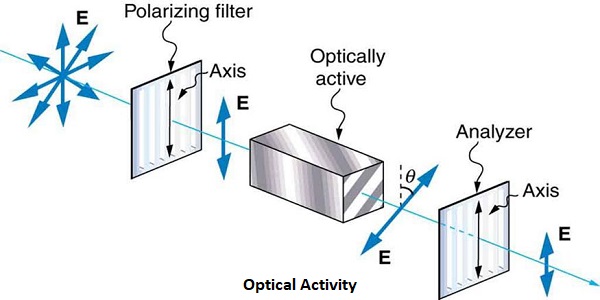
What is Optical Activity?
Optical activity, the ability of a substance to rotate the plane of polarization of a beam of light that is passed through it. (In plane-polarized light, the vibrations of the electric field are confined to a single plane.) The intensity of optical activity is expressed in terms of a quantity, called specific rotation, defined by an equation that relates the angle through which the plane is rotated, the length of the light path through the sample, and the density of the sample (or its concentration if it is present in a solution). Because the specific rotation depends upon the temperature and upon the wavelength of the light, these quantities also must be specified. The rotation is assigned a positive value if it is clockwise with respect to an observer facing the light source, negative if counter clockwise.
- A substance with a positive specific rotation is described as dextrorotatory and denoted by the prefix d or (+);
- one with a negative specific rotation is laevorotatory, designated by the prefix l or (-).