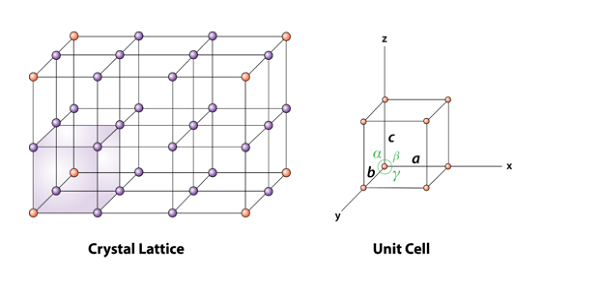
What is Unit Cell?
The simplest repeating unit in a crystal is called a unit cell. Each unit cell is defined in terms of lattice points the points in space about which the particles are free to vibrate in a crystal.
PRIMITIVE UNIT CELL
Unit cells in which the constituent particles are present only at the corners are called primitive unit cells.
NON-PRIMITIVE UNIT CELL
Unit cells in which the constituent particles are present not only at the corners of the cell but also at some other position.
TYPE OF NON-PRIMITIVE UNIT CELL
- Face centered
- End-centered
- Body centered
Face centered:
- The face centered cubic structure has atoms located at each of the corners and the centers of all the cubic faces
- Each of the corner atoms is the corner of another cube so the corner atoms are shared among eight unit cells.
- Additionally, each of its six face centered atoms is shared with an adjacent atom. Since 12 of its atoms are shared, it is said to have a coordination number of 12.
- The fcc unit cell consists of a net total of four atoms.
End-centered
- If one constituent particle lies at the centre of any two opposite faces besides the particles lying at the corners, it is known as End-Centred Unit Cell
Body centered:
- The body-centered cubic unit cell has atoms at each of the eight corners of a cube (like the cubic unit cell) plus one atom in the center of the cube.
- Each of the corner atoms is the corner of another cube so the corner atoms are shared among eight unit cells.
- It is said to have a coordination number of 8.
- The bcc unit cell consists of a net total of two atoms; one in the center and eight eighths from corners atoms.
