CONTINUUM HYPOTHESIS
A body consists of several particles. Each particle can be subdivided into molecules, atoms and electrons etc. It is not feasible to solve an engineering problem by treating a body as a conglomeration of such discrete particles. The body is assumed to consist of a continuous distribution of matter. In other words, body is treated as continuum.
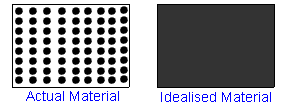
The mass density at a point P is a continuum is defined as the ratio of the mass element to the volume element ΔV enclosing the point , in the limit when tends to zero.
Note that, here the assumption is that mass is the continuous function of the volume. In the right picture of Fig.1, mass is not a continuous function of volume. In the limit, one may end up in a void.
Fig.1: Concept of continuum
This course will act as a foundation for fluid mechanics and solid mechanics courses. There, we deal with deformable bodies. In this course, we will be studying the behavior of rigid bodies under forces.
Rigid body:
A body is considered rigid when the changes in distance between any two of its points is negligible for the purpose at end or, A rigid body is a body that does not deform under the action of forces.
Deformable body:
A body is considered deformable when the changes in distance between any two of its points cannot be neglected.
Above mentioned assumptions are called Basic Assumptions of Classical Mechanics.