Voltage Measurements in Oscilloscope:
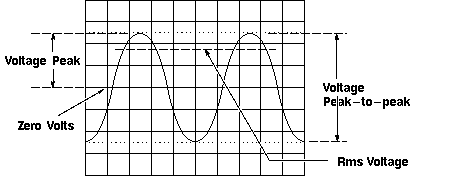
Voltage is the amount of electric potential, expressed in volts, between two points in a circuit. Usually one of these points is ground (zero volts) but not always. Voltages can also be measured from peak-to-peak – from the maximum point of a signal to its minimum point. You must be careful to specify which voltage you mean.
The oscilloscope is primarily a voltage-measuring device. Once you have measured the voltage, other quantities are just a calculation away. For example, Ohm’s law states that voltage between two points in a circuit equals the current times the resistance. From any two of these quantities you can calculate the third. Another handy formula is the power law: the power of a DC signal equals the voltage times the current. Calculations are more complicated for AC signals, but the point here is that measuring the voltage is the first step towards calculating other quantities.
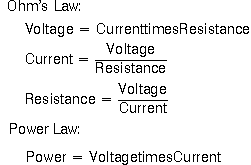
Method to Measure Voltage:
Voltage is the amount of electric potential between two points in a circuit. It is measured from peak-to-peak amplitude which measures the absolute difference between the maximum point of signal and its minimum point of the signal. The scope displays exactly the maximum and minimum voltage of the signal received. After measuring all high and low voltage points, scope calculates the average of the minimum and maximum voltage. But you must be careful to mention which voltage you mean. Normally, oscilloscope has fixed input range, but this can be easily increased with the use of simple potential divider circuit.
- The simplest way to measure signal is to set the trigger button to auto that means oscilloscope start to measure the voltage signal by identifying the zero voltage point or peak voltage by itself. As any of these two points identified the oscilloscope triggers and measure the range of the voltage signal.
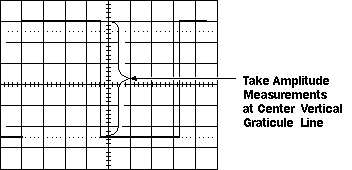
- Vertical and horizontal controls are adjusted so that the displayed image of the sine wave is clear and stable. Now take measurements along the centre vertical line which has the smallest divisions. Reading of the voltage signal will be given by vertical control.
Following figure shows the voltage of one peak – V[p] – and the peak-to-peak voltage – V[p-p] -, which is usually twice V[p]. Use the RMS (root-mean-square) voltage – V[RMS] – to calculate the power of an AC signal.
You take voltage measurements by counting the number of divisions a waveform spans on the oscilloscope’s vertical scale. Adjusting the signal to cover most of the screen vertically, then taking the measurement along the center vertical graticule line having the smaller divisions, makes for the best voltage measurements. The more screen area you use, the more accurately you can read from the screen.
Many oscilloscopes have on-screen cursors that let you take waveform measurements automatically on-screen, without having to count graticule marks. Basically, cursors are two horizontal lines for voltage measurements and two vertical lines for time measurements that you can move around the screen. A readout shows the voltage or time at their positions.
