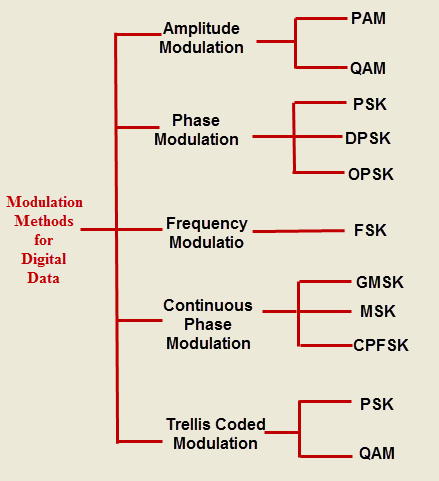
What is Modulation?
Modulation is nothing but, a carrier signal that varies in accordance with the message signal. Modulation technique is used to change the signal characteristics. Basically, the modulation is of following two types:
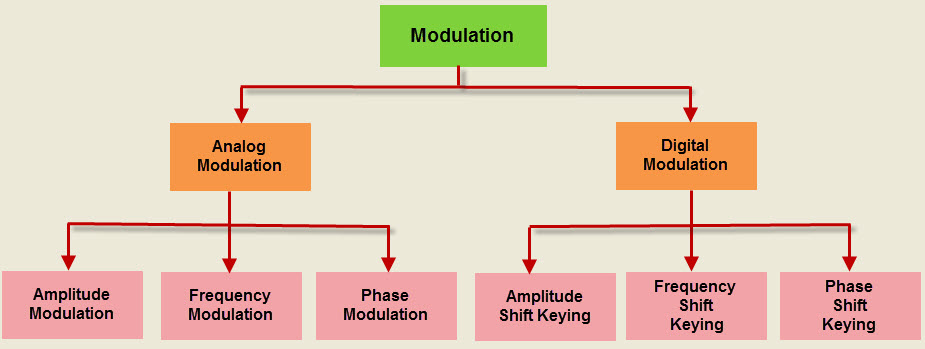
- Analog Modulation
- Digital Modulation
Analog Modulation:
In analog modulation, analog signal (sinusoidal signal) is used as a carrier signal that modulates the message signal or data signal. The general function Sinusoidal wave’s is shown in the figure below, in which, three parameters can be altered to get modulation – they are amplitude, frequency and phase; so, the types of analog modulation are:
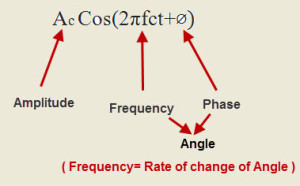
- Amplitude Modulation (AM)
- Frequency Modulation (FM)
- Phase Modulation (PM)
Amplitude Modulation:
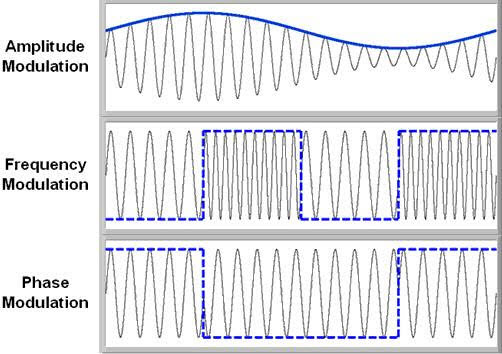
Amplitude modulation was developed in the beginning of the 20th century. It was the earliest modulation technique used to transmit voice by radio. This type of modulation technique is used in electronic communication. In this modulation, the amplitude of the carrier signal varies in accordance with the message signal, and other factors like phase and frequency remain constant.
Frequency Modulation:
In this type of modulation, the frequency of the carrier signal varies in accordance with the message signal, and other parameters like amplitude and phase remain constant. Frequency modulation is used in different applications like radar, radio and telemetry, seismic prospecting and monitoring newborns for seizures via EEG, etc.
Phase Modulation:
In this type of modulation, the phase of the carrier signal varies in accordance with the message signal. When the phase of the signal is changed, then it affects the frequency. So, for this reason, this modulation is also comes under the frequency modulation.
Digital Modulation:
For a better quality and efficient communication, digital modulation technique is employed. The main advantages of the digital modulation over analog modulation include available bandwidth , high noise immunity and permissible power. In digital modulation, a message signal is converted from analog to digital message, and then modulated by using a carrier wave.
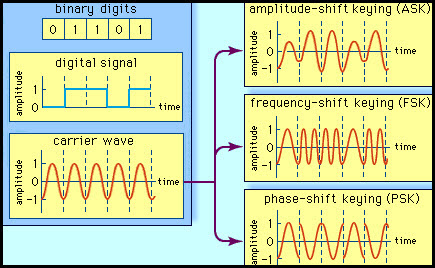
The carrier wave is switched on and off to create pulses such that the signal is modulated. Similar to the analog, in this system, the type of the digital modulation is decided by the variation of the carrier wave parameters like amplitude, phase and frequency.
The most important digital modulation techniques are based on keying such as:
Amplitude Shift Keying, Frequency Shift Keying, Phase Shift Keying, Differential Phase Shift Keying, Quadrature Phase Shift Keying, Minimum Shift Keying, Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying, Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing, etc., as shown in the figure.
In an Amplitude shift keying, the amplitude of the carrier wave changes based on the message signal or on the base-band signal, which is in digital format. It is sensitive to noise and used for low-band requirements.
In frequency shift keying, the frequency of the carrier wave is varied for each symbol in the digital data. It needs larger bandwidths as shown in the figure. Similarly, the phase shift keying changes the phase of the carrier for each symbol and it is less sensitive to noise.