What is Electric Resistance Welding?
Resistance welding is a liquid state welding process in which the metal to metal joint created in a liquid or molten state. It is a thermo-electric process in which heat is generated at the interface surfaces of welding plates due to electric resistance and controlled low pressure is applied to these plates to create a weld joint.
It is named as resistance welding because it uses electric resistance to produce heat. Resistance welding is a very efficient pollution-free welding process but its applications are limited due to its high equipment cost and limited material thickness.
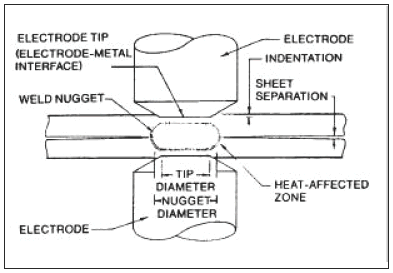
Principle:
All resistance welding like spot welding, seam welding, projection welding, etc. is worked on the same principle of heat generation due to electric resistance. When a current passes through electric resistance, it produces heat. This is the same principle that is used in the electric coil. The amount of heat produced depends on the resistance of the material, surface conditions, the current supplied, the time duration of current supplied, etc. This heat generation takes place due to the conversion of electric energy into thermal energy. The heat generation formula
is
H = I2RT
This heat is used to melt the interface metal to form a strong weld joint by fusion. This process produces weld without application of any filler material, flux and shielding gases.
Where,
H = Heat generated in joule R = Electric resistance in Ohm
I = Electric current in ampere T = Time of current flow in second
Types:
There are four main types of resistance welding. These are:
- Spot Welding
- Seam Welding
- Projection Welding
- Flash butt welding
