Introduction to TIG Welding:
TIG stands for tungsten inert gas welding or sometimes this welding is known as gas tungsten arc welding. In this welding process, the heat required to form a weld is provided by a very intense electric arc which is form between a tungsten electrode and workpiece. In this welding, a non-consumable electrode is used which does not melt.
Principle
In a TIG welding process, a high-intensity arc is produced between a tungsten electrode and workpiece. In this welding mostly the workpiece is connected to the positive terminal and the electrode is connected to the negative terminal. This arc produces heat energy which is further used to join metal plate by fusion welding. Shielding gas is also used which protect the weld surface from oxidization.
Equipment
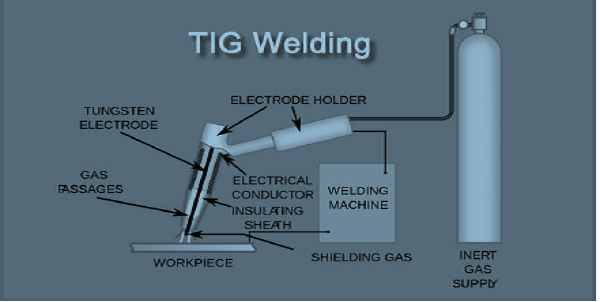
Power Source
A high current power source needed for TIG welding. It uses both AC and DC power sources. Mostly DC current is used for stainless steel, Mild Steel, Copper, etc. and AC current is used for aluminium, aluminium alloy and magnesium. The power source consists of a transformer, a rectifier, and electronic controls.
TIG Torch
It is the most important part of TIG welding. This torch has three main parts, tungsten electrode, collets and nozzle
Shielding Gas Supply System
Normally argon or other inert gases are used as shielded gas. The main purpose of shielded gas to protects the weld from oxidization.
Filler Material
Mostly for welding thin sheets no filler material is used. But for thick weld, the filler material is used. The filler material is used in form of rods which are directly fed into the weld zone manually.
Working
The working of TIG welding can be summarized as follow.
- First, a low voltage high current supply supplied by the power source to the welding electrode or tungsten electrode. Mostly, the electrode is connected to the negative terminal of the power source and the workpiece to the positive terminal.
- This current supplied from a spark between a tungsten electrode and workpiece. Tungsten is a non – consumable electrode, which gives a highly intense arc. This arc produced heat which melts the base metals to form a welding joint.
- The shielded gases like argon, helium is supplied through a pressure valve and regulating valve to the welding torch. These gases form a shield that does not allow any oxygen and other reactive gases into the weld zone. These gases also create a plasma which increases the heat capacity of the electric arc thus increases welding ability.
- For welding thin material no filler metal is required but for making a thick joint some filler material used in form of rods which fed manually by the welder into the welding zone.
